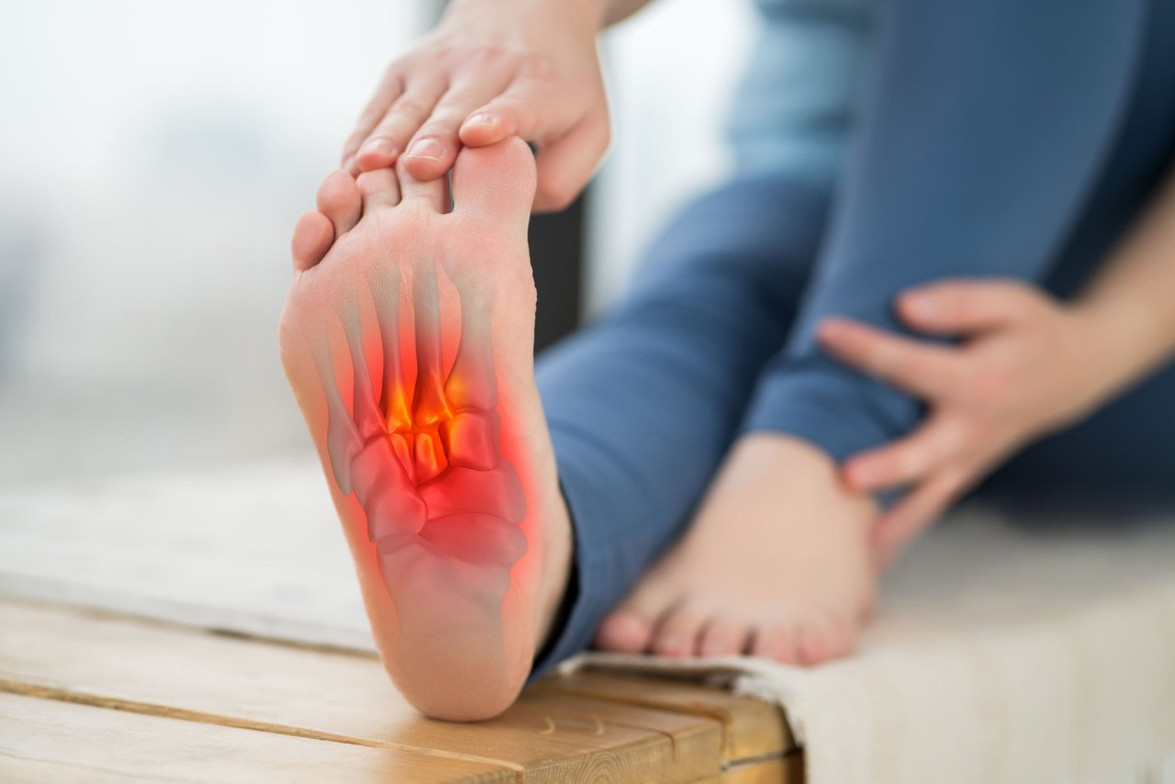
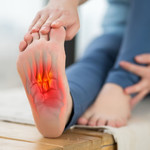
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes sharp or aching pain in the heel or bottom of the foot—especially with the first steps in the morning or after periods of standing. While many cases respond to basic care, persistent symptoms often require a more targeted, non-invasive treatment approach.
Understanding the Root Cause
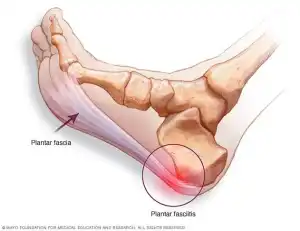
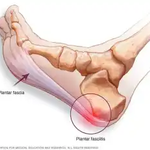
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia, the connective tissue that supports the arch of your foot, becomes irritated or overloaded. This may happen due to repetitive stress, improper footwear, tight calf muscles, or structural imbalances in the feet or lower legs.
A focused evaluation helps identify these contributing factors and guides a more effective care plan.
Conservative Treatment Options
Non-invasive care for plantar fasciitis typically includes:
-
Soft tissue therapies and myofascial work
-
Targeted stretching and mobility exercises
-
Gait and biomechanical support
-
Home care and activity modification
These therapies aim to reduce tension and irritation while allowing the tissue to heal and regain function.
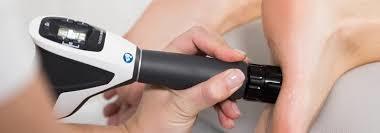
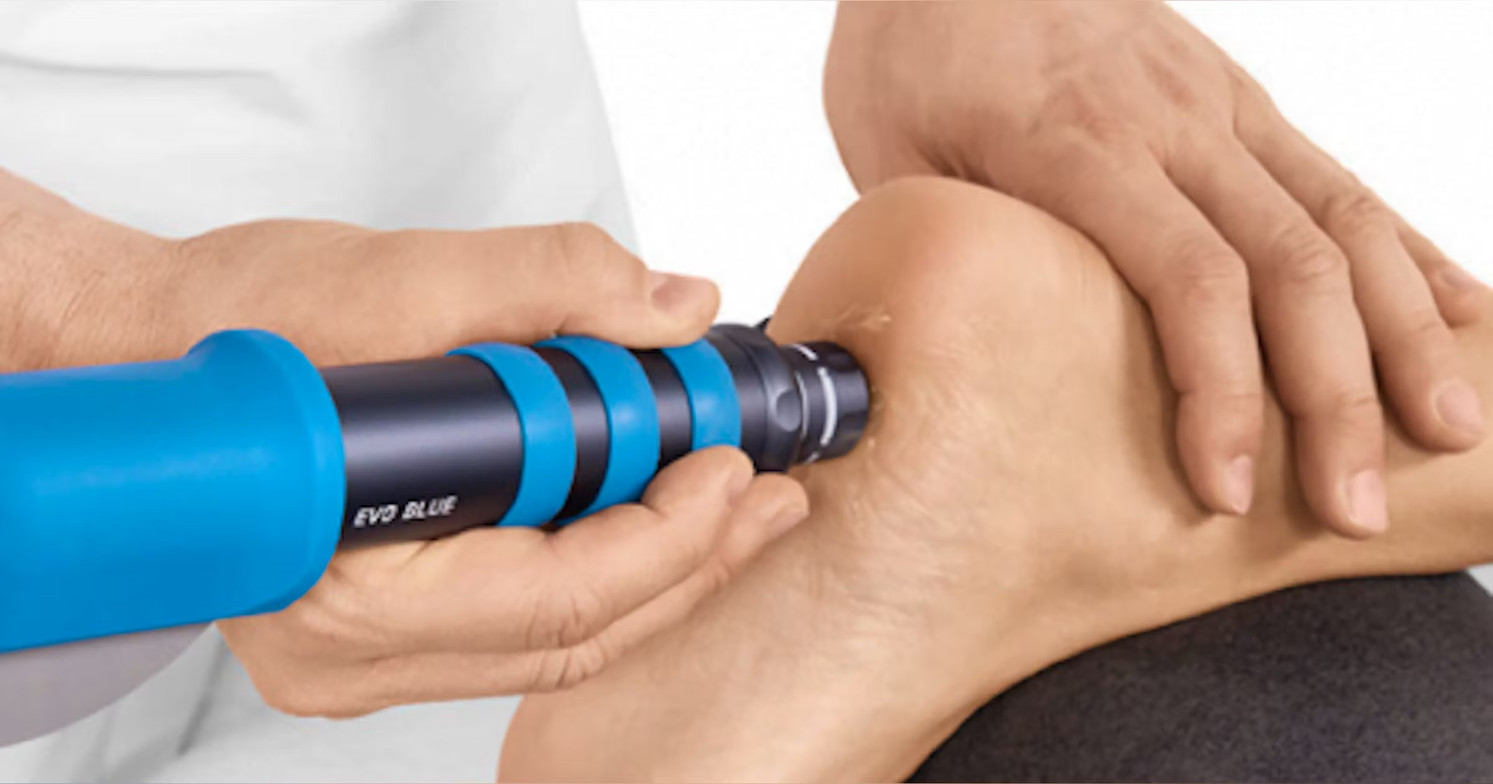
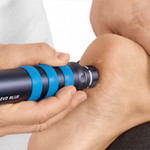
Shockwave Therapy for Chronic Cases
For patients with long-standing or treatment-resistant plantar fasciitis, shockwave therapy may be a valuable next step.
Radial shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses controlled acoustic pressure waves to:
-
Stimulate local circulation
-
Support cellular activity and tissue regeneration
-
Reduce chronic pain and inflammation
This in-office treatment does not require injections or surgery, and sessions are typically brief and well-tolerated.
Who May Benefit
Shockwave therapy may be appropriate for:
-
Active individuals with persistent heel pain
-
Patients not responding to stretching, orthotics, or rest
-
Those seeking to avoid injections or surgical intervention
A proper evaluation is required to determine if this treatment is right for you.
Supporting Long-Term Results
Shockwave therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis shows strong success rates, often ranging from 70% to over 90% in studies, with significant pain reduction seen within weeks and lasting for a year or more, making it an effective non-surgical option, especially for chronic cases, though results vary and full recovery takes time.
In addition to in-office care, we provide guidance on lifestyle and movement strategies to help prevent recurrence. This may include footwear recommendations, strengthening exercises, and adjustments to daily activity.
Our goal is to help you move with comfort and confidence—without relying on invasive interventions.
Take the First Step Toward Relief
If plantar fasciitis is making it difficult to walk, stand, or stay active, conservative care options—including shockwave therapy—may help you find relief.
Book a consultation to learn more about plantar fasciitis treatment options.

Jessica Walker, DC
Contact Me